Add custom context to AI agents
Overview
This guide demonstrates how to provide additional context to your AI agents beyond what's available through Port's integrations.
For this guide, we will leverage on the Incident Manager AI agent by adding Root Cause Analysis (RCA) documents to enable it to reference past incidents and their resolutions when answering questions.
Common use cases
- Provide historical context when responding to new incidents that are similar to past ones.
- Reference documented solutions and preventive measures from previous incidents.
- Help identify patterns across multiple incidents and suggest proactive measures.
- Store and access organizational knowledge in runbooks, architecture documents, and best practices.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes you have:
- A Port account with the AI agents feature enabled.
- An existing Incident Manager AI agent (or similar).
Set up data model
For this guide, we will create a custom blueprint to store RCA documents, populate it with sample data, and configure an existing AI agent to access this context.
Create Root Cause Analysis blueprint
We will create a custom blueprint to store RCA documents, populate it with sample data, and configure an existing AI agent to access this context.
Follow the steps below to create the blueprint:
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Blueprint. -
Click on
{...} Edit JSON. -
Copy and paste the JSON schema from below:
Root Cause AnalysisblueprintThe entities of this blueprint will represent different RCA documents from past incidents.
{
"identifier": "rootCauseAnalysis",
"title": "Root Cause Analysis",
"icon": "Bug",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"summary": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Summary",
"description": "Brief summary of the incident"
},
"incidentDate": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"title": "Incident Date",
"description": "When the incident occurred"
},
"severity": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Severity",
"enum": ["Critical", "High", "Medium", "Low"],
"enumColors": {
"Critical": "red",
"High": "orange",
"Medium": "yellow",
"Low": "green"
}
},
"affectedServices": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Affected Services",
"description": "Services impacted by this incident"
},
"rootCause": {
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"title": "Root Cause",
"description": "Detailed analysis of what caused the incident"
},
"resolution": {
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"title": "Resolution",
"description": "How the incident was resolved"
},
"preventiveMeasures": {
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"title": "Preventive Measures",
"description": "Actions taken to prevent similar incidents"
},
"lessonsLearned": {
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"title": "Lessons Learned",
"description": "Key takeaways and learnings from this incident"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags",
"description": "Tags for categorizing and searching RCAs"
}
},
"required": ["summary", "incidentDate", "severity", "rootCause", "resolution"]
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Click
Createto save the blueprint.
Populate with sample RCA data
Now let's populate the RCA blueprint with sample data that our AI agent can reference. You can ingest this data using any of these three methods:
- Port UI
- API
- Webhook
Database Connection Pool Exhaustion incident
Let's create our first RCA entity using the Port UI:
-
Go to your software catalog.
-
Find the "Root Cause Analysis" tab and click on
+ Root Cause Analysis. -
Toggle JSON mode and copy and paste the following JSON:
Database Connection Pool Exhaustion incident
{
"properties": {
"summary": "Payment service experienced 5-minute outage due to database connection pool exhaustion",
"incidentDate": "2024-01-15T14:20:00.000Z",
"severity": "High",
"affectedServices": [
"payment-service",
"checkout-service"
],
"tags": [
"payment-service",
"checkout-service"
],
"rootCause": "## Analysis\nThe payment service database connection pool was configured with a maximum of 10 connections. During peak traffic (Black Friday promotion), the service received 5x normal load, causing all connections to be exhausted.\n\n## Timeline\n- 14:30 - First alerts for payment service timeouts\n- 14:32 - Database monitoring showed 100% connection pool utilization \n- 14:35 - Root cause identified as connection pool exhaustion",
"resolution": "## Immediate Fix\n1. Increased database connection pool size from 10 to 50\n2. Restarted payment service instances\n3. Service restored at 14:35\n\n## Technical Details\n- Updated `application.yml` configuration\n- Deployed hotfix version 1.2.1\n- Verified connection pool metrics in monitoring dashboard",
"preventiveMeasures": "1. **Monitoring**: Added alerts for connection pool utilization >80%\n2. **Load Testing**: Implemented regular load testing with 10x normal traffic\n3. **Configuration**: Set connection pool size based on expected peak load + 50% buffer\n4. **Documentation**: Updated runbooks with connection pool troubleshooting steps",
"lessonsLearned": "- Always configure connection pools based on peak load, not average load\n- Monitor connection pool utilization as a key metric\n- Include database load in regular performance testing\n- Have connection pool size adjustment procedures documented"
},
"relations": {},
"icon": "Bug",
"identifier": "rca-db-pool-exhaustion-2024-01",
"title": "Database Connection Pool Exhaustion - Payment Service"
} -
Click
Createto save the RCA entity.
Memory Leak incident
Let us add another RCA entity:
-
Click on
+ Root Cause Analysis. -
Toggle JSON mode and copy and paste the following JSON:
Memory Leak incident
{
"properties": {
"summary": "Gradual memory leak in user service caused OOM crashes every 6 hours",
"incidentDate": "2024-02-08T09:15:00.000Z",
"severity": "Critical",
"affectedServices": [
"user-service",
"authentication-service"
],
"tags": [
"memory-leak",
"authentication",
"jvm"
],
"rootCause": "## Analysis\nThe user service authentication module had a memory leak in the session cache implementation. The cache was not properly clearing expired sessions, causing memory usage to grow continuously until OutOfMemory errors occurred.\n\n## Timeline\n- 09:15 - First OOM crash reported\n- 09:20 - Service automatically restarted\n- 15:15 - Second OOM crash (6 hours later)\n- 15:25 - Pattern identified, memory leak suspected",
"resolution": "## Immediate Fix\n1. Implemented proper session cleanup in authentication cache\n2. Added memory monitoring and alerting\n3. Deployed hotfix version 2.1.3\n4. Increased heap size as temporary measure\n\n## Technical Details\n- Fixed session expiration logic in AuthenticationCache.java\n- Added automated cleanup job running every 30 minutes\n- Configured JVM garbage collection tuning",
"preventiveMeasures": "1. **Memory Monitoring**: Added heap usage alerts at 80% and 90% thresholds\n2. **Code Review**: Enhanced review process to check for potential memory leaks\n3. **Testing**: Added memory leak detection to integration test suite\n4. **Documentation**: Created memory management guidelines for developers",
"lessonsLearned": "- Always implement proper cleanup mechanisms for caches and session storage\n- Memory monitoring should be a standard part of service deployment\n- Regular heap dumps and analysis can help identify memory issues early\n- Consider using weak references for cache implementations to allow garbage collection"
},
"relations": {},
"icon": "Bug",
"identifier": "rca-memory-leak-user-service-2024-02",
"title": "Memory Leak in User Service Authentication Module"
} -
Click
Createto save the RCA entity.
Database Connection Pool Exhaustion incident
You can create RCA entities programmatically using Port's API. This approach is useful for:
- Bulk imports: Adding multiple RCA documents at once
- CI/CD integration: Automatically creating RCAs as part of your deployment pipeline
- Custom scripts: Building tools to migrate data from existing systems
Where to run this code:
- Local scripts: Run on your development machine for one-time imports
- CI/CD pipelines: Integrate into GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins jobs
- Automation servers: Deploy as scheduled jobs or triggered workflows
- Migration tools: Part of data migration scripts when moving from other systems
First, get your API credentials and token:
import requests
# Get API token
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'}
# Create RCA entity
rca_entity = {
"properties": {
"summary": "Payment service experienced 5-minute outage due to database connection pool exhaustion",
"incidentDate": "2024-01-15T14:20:00.000Z",
"severity": "High",
"affectedServices": [
"payment-service",
"checkout-service"
],
"tags": [
"payment-service",
"checkout-service"
],
"rootCause": "## Analysis\nThe payment service database connection pool was configured with a maximum of 10 connections. During peak traffic (Black Friday promotion), the service received 5x normal load, causing all connections to be exhausted.\n\n## Timeline\n- 14:30 - First alerts for payment service timeouts\n- 14:32 - Database monitoring showed 100% connection pool utilization \n- 14:35 - Root cause identified as connection pool exhaustion",
"resolution": "## Immediate Fix\n1. Increased database connection pool size from 10 to 50\n2. Restarted payment service instances\n3. Service restored at 14:35\n\n## Technical Details\n- Updated `application.yml` configuration\n- Deployed hotfix version 1.2.1\n- Verified connection pool metrics in monitoring dashboard",
"preventiveMeasures": "1. **Monitoring**: Added alerts for connection pool utilization >80%\n2. **Load Testing**: Implemented regular load testing with 10x normal traffic\n3. **Configuration**: Set connection pool size based on expected peak load + 50% buffer\n4. **Documentation**: Updated runbooks with connection pool troubleshooting steps",
"lessonsLearned": "- Always configure connection pools based on peak load, not average load\n- Monitor connection pool utilization as a key metric\n- Include database load in regular performance testing\n- Have connection pool size adjustment procedures documented"
},
"relations": {},
"icon": "Bug",
"identifier": "rca-db-pool-exhaustion-2024-01",
"title": "Database Connection Pool Exhaustion - Payment Service"
}
# Create the entity
response = requests.post(
f'{API_URL}/blueprints/rootCauseAnalysis/entities',
json=rca_entity,
headers=headers
)
if response.status_code == 201:
print("RCA entity created successfully!")
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
Memory Leak incident
Let's add the second RCA entity:
# Memory leak RCA entity
memory_leak_entity = {
"properties": {
"summary": "Gradual memory leak in user service caused OOM crashes every 6 hours",
"incidentDate": "2024-02-08T09:15:00.000Z",
"severity": "Critical",
"affectedServices": [
"user-service",
"authentication-service"
],
"tags": [
"memory-leak",
"authentication",
"jvm"
],
"rootCause": "## Analysis\nThe user service authentication module had a memory leak in the session cache implementation. The cache was not properly clearing expired sessions, causing memory usage to grow continuously until OutOfMemory errors occurred.\n\n## Timeline\n- 09:15 - First OOM crash reported\n- 09:20 - Service automatically restarted\n- 15:15 - Second OOM crash (6 hours later)\n- 15:25 - Pattern identified, memory leak suspected",
"resolution": "## Immediate Fix\n1. Implemented proper session cleanup in authentication cache\n2. Added memory monitoring and alerting\n3. Deployed hotfix version 2.1.3\n4. Increased heap size as temporary measure\n\n## Technical Details\n- Fixed session expiration logic in AuthenticationCache.java\n- Added automated cleanup job running every 30 minutes\n- Configured JVM garbage collection tuning",
"preventiveMeasures": "1. **Memory Monitoring**: Added heap usage alerts at 80% and 90% thresholds\n2. **Code Review**: Enhanced review process to check for potential memory leaks\n3. **Testing**: Added memory leak detection to integration test suite\n4. **Documentation**: Created memory management guidelines for developers",
"lessonsLearned": "- Always implement proper cleanup mechanisms for caches and session storage\n- Memory monitoring should be a standard part of service deployment\n- Regular heap dumps and analysis can help identify memory issues early\n- Consider using weak references for cache implementations to allow garbage collection"
},
"relations": {},
"icon": "Bug",
"identifier": "rca-memory-leak-user-service-2024-02",
"title": "Memory Leak in User Service Authentication Module"
}
# Create the second entity
response = requests.post(
f'{API_URL}/blueprints/rootCauseAnalysis/entities',
json=memory_leak_entity,
headers=headers
)
if response.status_code == 201:
print("Second RCA entity created successfully!")
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
Example integration scenarios:GitHub Actions workflow
name: Create RCA from Issue
on:
issues:
types: [closed]
jobs:
create-rca:
if: contains(github.event.issue.labels.*.name, 'post-mortem')
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Create RCA Entity
run: |
python -c "
import requests
import os
# API setup
credentials = {
'clientId': '${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}',
'clientSecret': '${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}'
}
token_response = requests.post('https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'}
# Create RCA from issue data
rca_entity = {
'identifier': 'rca-${{ github.event.issue.number }}',
'title': '${{ github.event.issue.title }}',
'properties': {
'summary': '${{ github.event.issue.title }}',
'incidentDate': '${{ github.event.issue.created_at }}',
'severity': 'Medium',
'rootCause': '''${{ github.event.issue.body }}''',
'tags': ['github-issue']
}
}
response = requests.post(
'https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/rootCauseAnalysis/entities',
json=rca_entity,
headers=headers
)
print(f'RCA created: {response.status_code}')
"Standalone Python script for bulk import
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Bulk import RCA documents from CSV or JSON files
Usage: python bulk_import_rcas.py --file rcas.csv
"""
import requests
import csv
import argparse
import os
from datetime import datetime
def get_port_token():
"""Get Port API token"""
credentials = {
'clientId': os.getenv('PORT_CLIENT_ID'),
'clientSecret': os.getenv('PORT_CLIENT_SECRET')
}
response = requests.post('https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
return response.json()['accessToken']
def create_rca_from_csv_row(row, headers):
"""Create RCA entity from CSV row"""
return {
'identifier': f"rca-{row['incident_id']}",
'title': row['title'],
'properties': {
'summary': row['summary'],
'incidentDate': row['incident_date'],
'severity': row['severity'],
'affectedServices': row['affected_services'].split(','),
'rootCause': row['root_cause'],
'resolution': row['resolution'],
'preventiveMeasures': row['preventive_measures'],
'lessonsLearned': row['lessons_learned'],
'tags': row['tags'].split(',') if row['tags'] else []
}
}
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Bulk import RCA documents')
parser.add_argument('--file', required=True, help='CSV file containing RCA data')
args = parser.parse_args()
# Get API token
access_token = get_port_token()
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'}
# Process CSV file
with open(args.file, 'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for row in reader:
rca_entity = create_rca_from_csv_row(row, reader.fieldnames)
response = requests.post(
'https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/rootCauseAnalysis/entities',
json=rca_entity,
headers=headers
)
if response.status_code == 201:
print(f"✓ Created RCA: {rca_entity['title']}")
else:
print(f"✗ Failed to create RCA: {response.text}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Create webhook integration
You can automatically create RCA entities from external systems using Port's webhook integration.
This approach enables seamless integration with your existing tools and workflows for real-time data ingestion.
Create the webhook
-
Go to the data sources page.
-
Click
+ Data source→Webhook→Custom integration. -
Fill in the webhook details:
- Title:
RCA Webhook Integration - Identifier: Leave auto-generate enabled or set to
rcaWebhook - Description:
Automatically create RCA entities from external systems - Icon: Select an appropriate icon (e.g., Webhook or Bug)
- Title:
-
Click
Nextto proceed to the mapping configuration.
Step 2: Configure the webhook URL
You'll see your unique webhook URL that external systems will use:
https://ingest.getport.io/YOUR_WEBHOOK_KEY
Step 3: Configure the mapping
In the mapping section, replace the default configuration with:
[
{
"blueprint": "rootCauseAnalysis",
"operation": "create",
"filter": ".body.event_type == \"post_mortem_created\"",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.incident_id | tostring",
"title": ".body.title",
"properties": {
"summary": ".body.summary",
"incidentDate": ".body.incident_date",
"severity": ".body.severity",
"affectedServices": ".body.affected_services",
"tags": ".body.tags",
"rootCause": ".body.root_cause",
"resolution": ".body.resolution",
"preventiveMeasures": ".body.preventive_measures",
"lessonsLearned": ".body.lessons_learned"
}
}
}
]
Test the mapping
-
In the "Add test event" section, you can paste a sample JSON payload to test your mapping.
-
Use this test payload:
{
"headers": {},
"body": {
"event_type": "post_mortem_created",
"incident_id": "rca-test-incident-001",
"title": "Test RCA - Database Connection Pool Exhaustion",
"summary": "Test incident for webhook integration",
"incident_date": "2024-01-15T14:20:00.000Z",
"severity": "High",
"affected_services": ["payment-service", "checkout-service"],
"tags": ["test", "database"],
"root_cause": "Database connection pool exhaustion during peak traffic",
"resolution": "Increased connection pool size and restarted services",
"preventive_measures": "Added monitoring and alerts for connection pool utilization",
"lessons_learned": "Always configure connection pools based on peak load"
},
"queryParams": {}
}
-
Click
Test mappingto validate that your configuration correctly creates an RCA entity. -
Once the test passes, click
Saveto create your webhook integration.
Configure security (optional)
If you need to secure your webhook, you can configure authentication in the Settings tab:
- Secret: Set a shared secret for signature validation
- Signature Header: Specify the header containing the signature
- Algorithm: Choose the hashing algorithm (sha256 recommended)
Send data to webhook
Once your webhook is configured and saved, external systems can send POST requests to your webhook URL to automatically create RCA entities:
curl -X POST "https://ingest.getport.io/YOUR_WEBHOOK_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"event_type": "post_mortem_created",
"incident_id": "rca-db-pool-exhaustion-2024-01",
"title": "Database Connection Pool Exhaustion - Payment Service",
"summary": "Payment service experienced 5-minute outage due to database connection pool exhaustion",
"incident_date": "2024-01-15T14:20:00.000Z",
"severity": "High",
"affected_services": ["payment-service", "checkout-service"],
"tags": ["payment-service", "checkout-service"],
"root_cause": "## Analysis\nThe payment service database connection pool was configured with a maximum of 10 connections. During peak traffic, all connections were exhausted.",
"resolution": "## Immediate Fix\n1. Increased database connection pool size from 10 to 50\n2. Restarted payment service instances",
"preventive_measures": "1. **Monitoring**: Added alerts for connection pool utilization >80%\n2. **Load Testing**: Implemented regular load testing",
"lessons_learned": "- Always configure connection pools based on peak load, not average load\n- Monitor connection pool utilization as a key metric"
}'
For a more comprehensive knowledge base, consider adding 5-10 RCA documents covering different types of incidents your organization has experienced.
Update AI agent configuration
Now we'll modify the Incident Manager AI agent to include access to our RCA documents.
Add RCA blueprint to allowed blueprints
-
Go to the AI Agents page.
-
Find the Incident Manager agent and click on the
...on the far right of the row. -
Click on
Edit. -
In the
allowed_blueprintsarray, add"rootCauseAnalysis":"allowed_blueprints": [
"pagerdutyService",
"pagerdutyIncident",
"pagerdutyEscalationPolicy",
"pagerdutySchedule",
"pagerdutyOncall",
"pagerdutyUser",
"_user",
"_team",
"service",
"rootCauseAnalysis" //highlight
] -
Click
Saveto save the changes.
Update the agent prompt
Enhance the prompt to include instructions about using RCA context:
-
Click on
Edit propertyon thePromptfield. -
Replace the existing content with the following:
Enhanced agent prompt
You are an agent responsible for answering questions about PagerDuty incidents, services, escalation policies, schedules, and on-call rotations.
You also have access to historical Root Cause Analysis (RCA) documents from past incidents.
## Guidelines
- Provide clear information about incidents
- Identify who is on-call for services (both primary and secondary on-call)
- Report on incident statistics and resolution times
- When relevant, reference past RCA documents to provide context and suggest solutions
- Use RCA lessons learned to help prevent similar incidents
- Suggest preventive measures based on historical incident patterns -
Click
Saveto save the changes.
Add RCA-focused conversation starters
-
Click on
Edit propertyon theConversation startersfield. -
Replace the existing content with the following:
Conversation starters
[
"Who is on call for the payment service?",
"What are the active incidents right now?",
"What is our average incident resolution time?",
"Have we seen database connection issues before?",
"What can we learn from past payment service incidents?",
"Show me RCAs for incidents similar to the current one"
] -
Click
Save propertyto save the changes. -
Click on
Updateto save the changes to the agent.
You can now use these RCA context in your agent's responses:
- Search RCA documents when users ask about similar past incidents.
- Reference specific resolution steps from past incidents when applicable.
- Highlight patterns across multiple incidents.
- Suggest preventive measures from historical data.
Test the enhanced agent
Let's test that our agent can now reference RCA documents with some example questions.
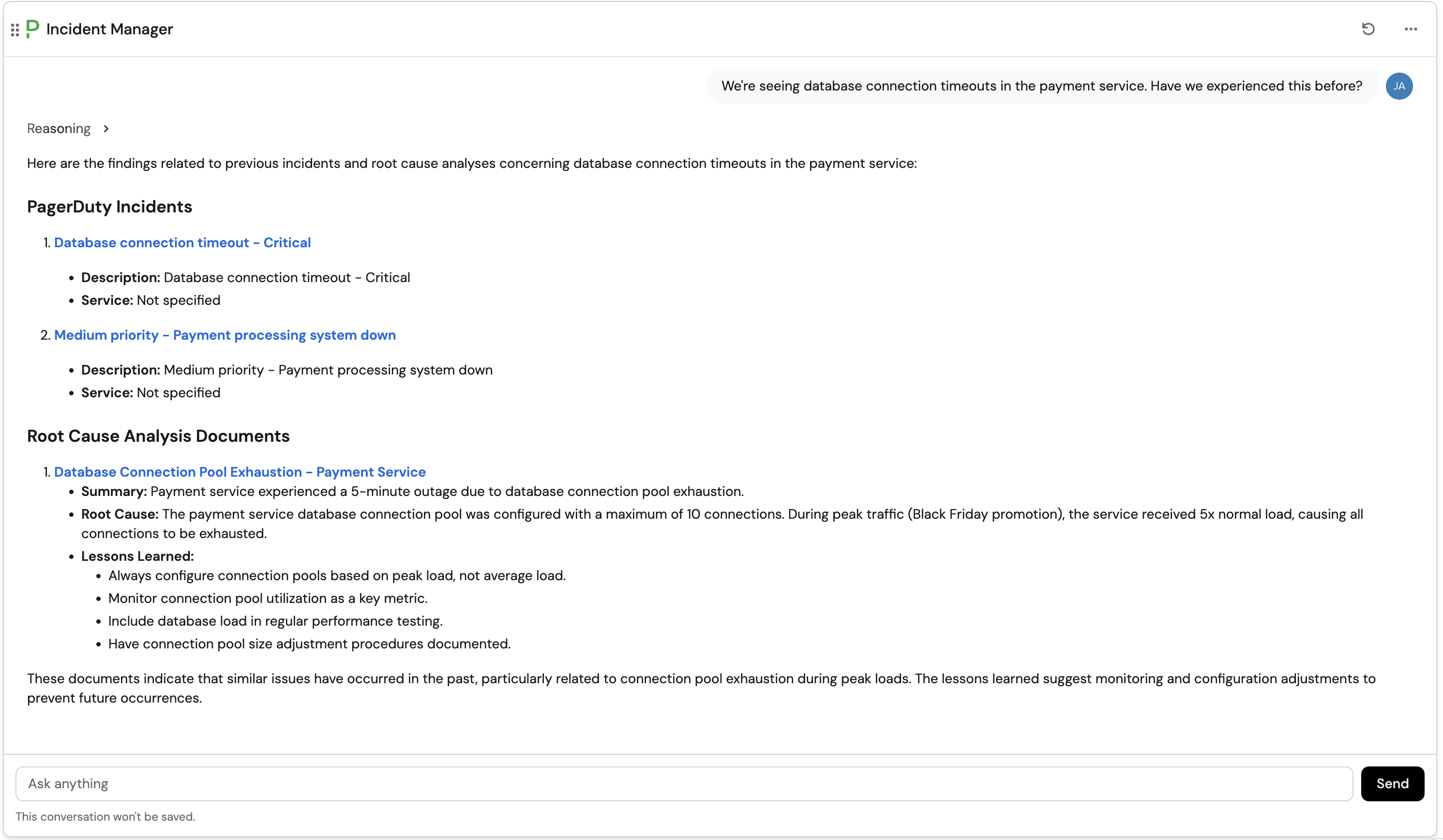
Question: "We're seeing database connection timeouts in the payment service. Have we experienced this before?"
Expected response: The agent should reference the RCA document we created and provide details about the previous database connection pool exhaustion incident, including the resolution steps and preventive measures.
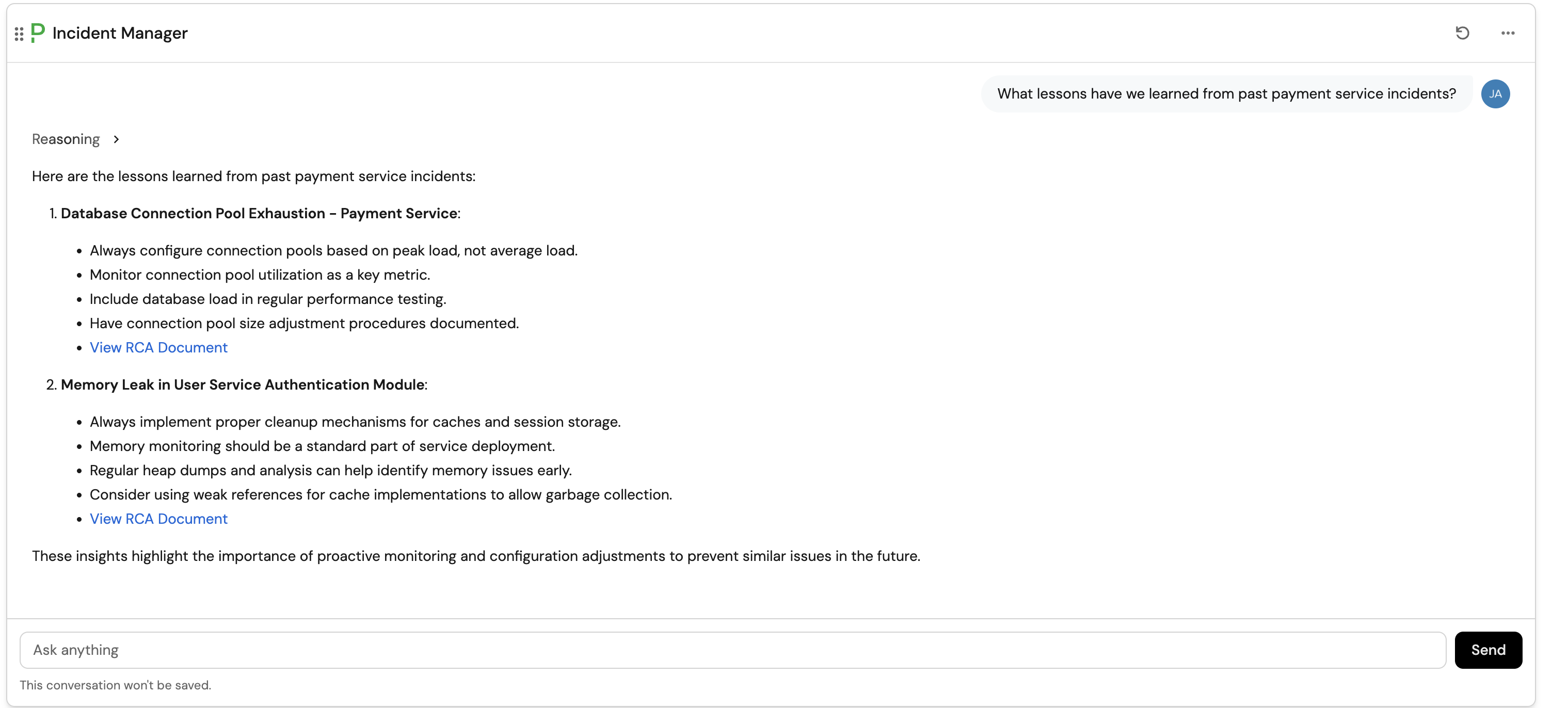
Question: "What lessons have we learned from past payment service incidents?"
Expected response: The agent should search through RCA documents tagged with payment-related services and summarize key lessons learned.
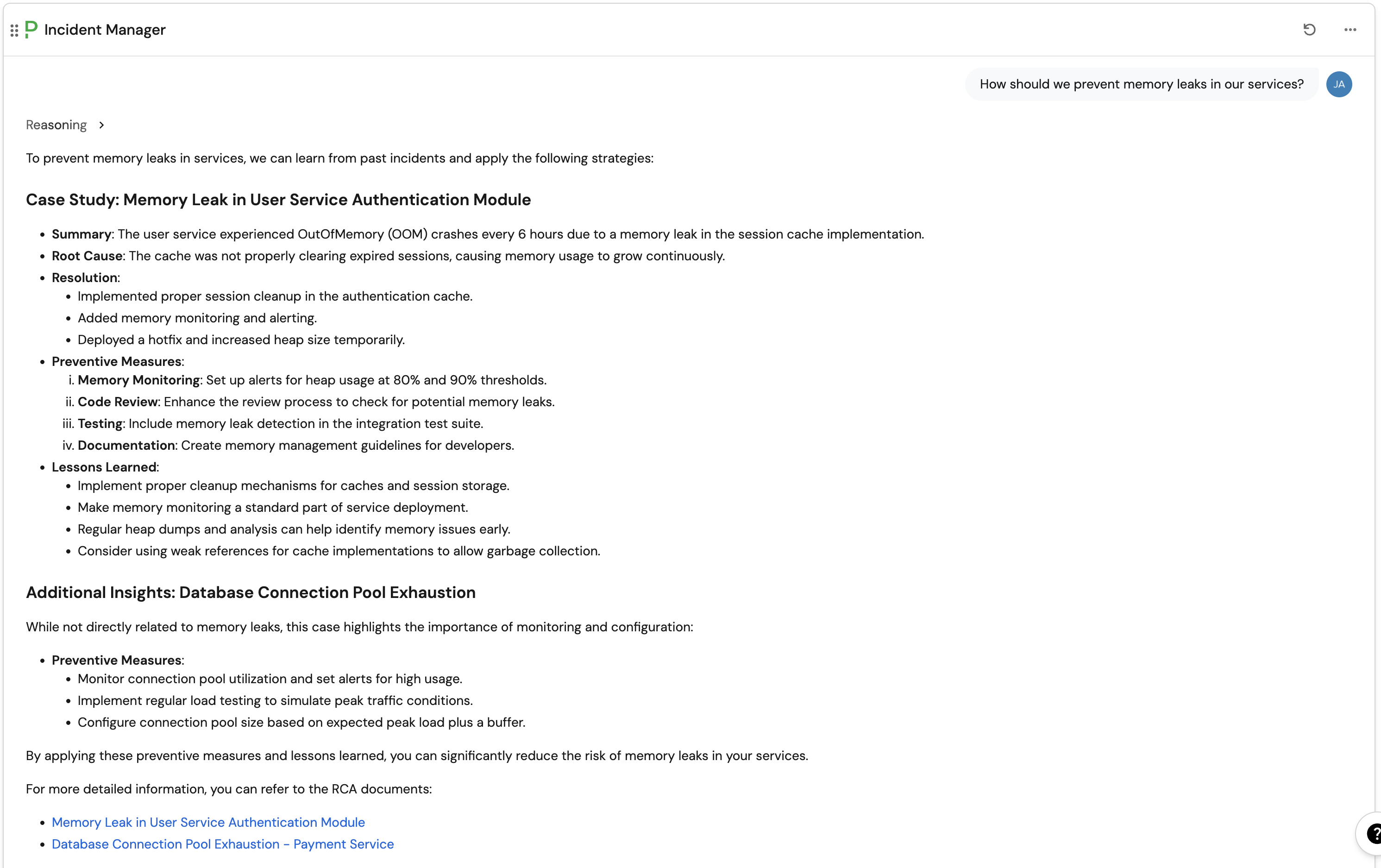
Question: "How should we prevent memory leaks in our services?"
Expected response: The agent should reference preventive measures from relevant RCA documents.
Conclusion
You have successfully enhanced your AI agent with custom context using entities! Your Incident Manager agent now has access to historical incident knowledge, making it significantly more valuable for both current incident response and prevention of future issues.
The approach we've demonstrated here can be extended to other types of documentation:
- Runbooks: Create a "Runbook" blueprint with markdown procedures.
- Architecture docs: Store system architecture information.
- Process documentation: Include incident response procedures.
- Best practices: Capture organizational standards and guidelines.
Additional ideas
Beyond incident management, you can use the same approach to enhance your AI agents with various types of organizational knowledge:
Documentation Agent
Create a "Documentation" blueprint to store:
- API documentation: Store OpenAPI specs, endpoint descriptions, and usage examples.
- Onboarding guides: New team member checklists and getting-started resources.
- Technical standards: Coding standards, architectural patterns, and best practices.
"Where can I find the API documentation for the user authentication service?"
Deployment Agent
Create a "Deployment Guide" blueprint to store:
- Environment-specific configs: Production, staging, and development deployment procedures.
- Release notes: Feature descriptions, breaking changes, and migration guides.
- Rollback procedures: Step-by-step recovery instructions for different scenarios.
"What's the rollback procedure for the payment service in production?"
Security Agent
Create a "Security Policy" blueprint to store:
- Compliance requirements: SOC2, GDPR, and other regulatory guidelines.
- Security reviews: Vulnerability assessments and remediation procedures.
- Access control policies: Permission matrices and approval workflows.
"What are the security requirements for handling customer data?"
Knowledge Base Agent
Create a "FAQ" or "Knowledge Article" blueprint to store:
- Common issues: Frequently asked questions and their solutions.
- Troubleshooting guides: Step-by-step diagnostic procedures.
- Team knowledge: Tribal knowledge, tips, and tricks from experienced team members.
"How do I debug slow database queries in our application?"
Begin with one additional use case that addresses your team's most common questions, then gradually expand to cover more areas as you see value from the AI agent interactions.
Next steps
Here are some ways to expand and improve your setup:
- Automate RCA creation: Set up automations to create RCA entities from incident post-mortems.
- Cross-reference data: Link RCAs to services, teams, and other relevant entities using relations.
- Monitor agent usage: Review AI invocation logs to see how effectively the agent uses RCA context.
- Add more context types: Create additional blueprints for different types of organizational knowledge.
- Regular maintenance: Periodically review and update RCA documents as processes evolve.